Marketing: Perceptual/Position Mapping
Branding an organization is one of the critical functions of the marketing department. Revieiwng the company (product) brand in relation to competitors and getting a clear vision of where the brand is situated helps identify many elements of the marketing strategy. Creating a perceptual/position map provides a graphic illustration of the organization/product position within the market place where it is competing.
Positioning is one of the real skills in good marketing. Do it well and the 4Ps fall into place. (Nowell, 2005)
Branding
Creating a brand and image for a product or service is one of the key activities of marketing. There are a variety of strategies that can be adopted to create the brand including but not limited to: highest quality, least expensive, best value, most prestigious, fastest, safest etc. (Nykiel, 2005, P. 39) Each of these strategies will define the organizations category membership however it is the brand that will help bring customers to the door. For instance, gasoline is a product that is pretty much identical no matter what particular brand one buys yet consumers will go out of their way to fuel up at their chosen outlet. There are a variety of opinions about the components of a brand, but most lists will have some variation of:
- Functions -What the brand can do, its core mechanical purpose. For a hotel this might be to provide a place to sleep.
- Benefits -What consumers can gain from using / owning the brand. For a hotel this might be feeling relaxed after a good night’s sleep.
- Associations -What consumers link or connect the brand to. For a hotel this might be a thing as diverse as: events held there, celebrity guests, or the town it is located in.
- Personality -What kind of human characteristics the brand possesses. For a hotel this might be a thing like: fun, reliability, liveliness, romanticism.
- Promise -What consumers believe the brand says it is delivering. For a hotel this might include: a tropical paradise or maybe five-star service. (Molesworth, Scullion & Dengri-Knott)
Creating the brand is not the end of the exercise. In a competitive market it is equally important to position your product or service relative to the competition (learnmarketing.net).
Points of Parity and Points of Difference
Positioning a brand requires considerable thought and discussion. Amongst the variables one needs to consider is a close look at Points of Differences (POD) and Points of Parity (POP) that an organization has to the competition in the market category. The key variables are the POD’s which serve to differentiate the company from its competitors. They represent “attributes or benefits consumers strongly associate with a brand, positively evaluate and believe they cannot find to the same extent with a competitive brand” (Kotler & Keller, 2006, p. 312). POP’s come in two varieties: Competitive, which seek to negate a competitor’s points of difference and category, which play up “the attributes that consumers view as essential to membership in the category” (Kotler & Keller, 2006, p. 313)
Exploring Tim Hortons Inc.
Tim Hortons Inc provides an example of branding and brand position that takes into account all these various elements.
Tim Hortons Inc. is quick-service restaurant chain in Canada. The Company's menu offerings include premium coffee, flavored cappuccinos, specialty teas, home-style soups, sandwiches and baked goods, including donuts, bagels, muffins, cookies, croissants and pastries. Tim Hortons restaurants operate in a variety of formats. A standard Tim Hortons restaurant is a freestanding building, ranging in size from 1,400 to 3,090 square feet with a drive-thru window. (Reuters News: Business and Finance)
The description is accurate but it places Tim Hortons squarely in the “fast food restaurant” category and misses that the organization “is the top seller of brewed coffee in Canada, and derives close to half of its sales from the hot liquid”(Shaw, 2006) which means Tim Hortons must work hard at positioning relative to the competitors in this particular category in order to keep that market share. The organization started out as a donut /coffee shop so much of the branding springs from those roots and new products have enjoyed success based on the brand. “Always Fresh” is the theme of the chain as is the constant connection of the company and its products to hockey, with a specific emphasis on kids hockey. Connecting the national sport to family values, fresh products and quick service has been the foundation of the brand since the early days.
Details of the positioning map
One of the most difficult aspects of creating a positioning map is deciding on the parameters used for the axis. They have to be relevant to the consumer and define some specific attributes that will help the organization define itself relative to the competition. The marketing program on the Bournemouth University instructional site (Molesworth, Scullion & Dengri-Knott) provided a useful set of criteria for a positioning map for Tim Hortons Inc. The vertical axis describes the environment (comfortable vs. fast delivery) while the horizontal axis focuses on the size of product choice.
Descriptions of the competitor’s position
The competitors in the category of “coffee shop” include Starbucks, Second Cup, and Country Style Donuts as well as a host of smaller franchises and privately-owned operations. Starbucks, Second Cup and many of the privately-owned businesses are located in large urban areas and seek to position themselves by choice of product and shopping experience. Country Style Donuts, many of the smaller franchise groups, and other private business are rural or small-town enterprises. Country Style chose to offer the same service and product as Tim Hortons but located in centers that where originally outside the business areas which interested Tim Hortons.
Positioning Map: Tim Hortons Inc.
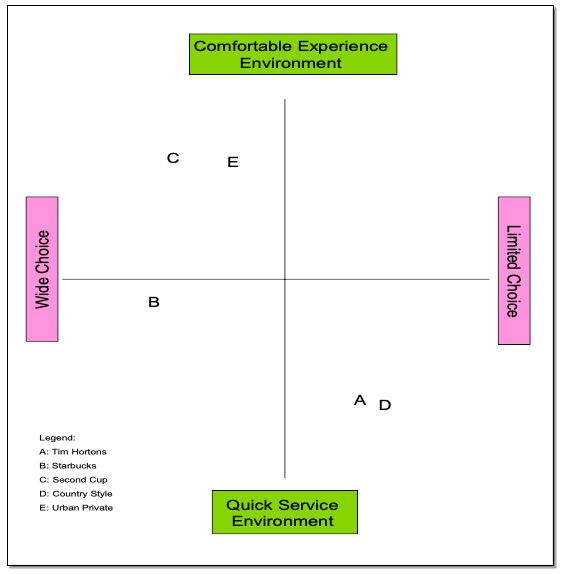
Tim Hortons– fast service environment, limited choice, some specialty products such as “ice Cappuccino”
Starbucks– fast service, wide choice of blends, specialty coffees including lattes, cappuccino, espresso
Second Cup– comfortable experience environment, wide choice of blends
Urban private business– comfortable experience environment, some choice and usually custom blended beans, specialty coffees such as lattes, cappuccino and espresso.
Country Style Donuts – Same product, pricing and experience as Tim Hortons but serving a different geographic market.
Rural Private Business – a mixed bag of offerings. Very difficult to map since they tend to respond to the neighborhood.
Conclusion
The use of a perceptual or positioning map can be a useful graphic illustration of the market position a company wishes to occupy. More importantly it is a simple way to illustrate where the competition is positioned and to point out where market share can be expanded. This particular map points out both this advantage and a potential flaw if the axis are not carefully thought through.
Tim Hortons has recognized the challenge that Starbucks brings to the table and is responding by increasing choice. The position map clearly indicates that there is room form Tim Hortons to move into the market segment staked out by Starbucks but offering more choice in products. This will also position them more favorably against Second Cup along one axis. They have begun to shift their position slightly to recapture lost market share and to attract some customers away from Starbucks. On the other hand they are not going to alter the environment since this will impact on the other customer demands for quick service. The move towards the comfortable environment fostered by Second Cup would require a reconfiguration of the restaurants to provide seating other than service tables (i.e. armchairs and sofas).
The relationship of Country Style and Tim Hortons on this positioning map provides a false impression. Based on this axis the two organizations are set up to attract the same clients however they serve a different geographic market segment so could coexist in their own niche. This single difference points out the importance of creating a perception/positioning map that compares the correct elements of the positioning strategy in relations to the competition.
Author: David Johnson, student LIGS University
Bibliography:
Kotler, P. & Keller, K.L. (2006) , Marketing Management (12thed.). New Jersey: Prentice Hall
Learn Marketing.net. For marketing learners globally, Positioning, Retrieved January 6, 2007 fromhttp://www.learnmarketing.net/positioning.htm
Molesworth, M., Scullion, R. & Dengri-Knott , J. Marketing: Branding, Brand Components. Retrieved January 3, 2008 from Bournemouth University “Foundation Degree South West” http://media3.bournemouth.ac.uk/marketing/10branding/03components.html
Nowell, David (2005), Staking Your Position. Retrieved January 3, 2008 from Sheridan College, David Nowell’s Home Page. http://www.sheridanc.on.ca/~nowell/markstuf/position/position.htm
Nykiel, Ronald A., (2005) Hospitality Management Strategies. New Jersey: Prentice Hall
Reuters News: Business and Finance: US Stocks Tim Hortons Inc, Retrieved December 31, 2006 from http://stocks.us.reuters.com/stocks/fullDescription.asp?rpc=66&symbol=THI
Shaw, H. (2006, January 6) Tim Hortons tiptoes into Starbucks territory, Financial Post.Retrieved December 28, 2006 from http://www.financialpost.com/story.html?id=4cdae04b-4380-4d7c-9faa-753a8d711dad&p=1