Network Operation with and without Quality of Service (QoS) Technology and their Impacts to the Organization
Technology is the key driver that influences and impacts how our business is operating now a day. It is important for the organizaton to realize and research into the investments in technology and their impact in the business such as network operation center (NOC), command and control center, internet service provider (ISP) organization.
Author: Minh Nguyen D.
Introduction
Technology is the key driver that influences and impacts how our business is operating now a day. It is important for the organizaton to realize and research into the investments in technology and their impact in the business such as network operation center (NOC), command and control center, internet service provider (ISP) organization. It is critical to assess how technology, specifically, the quality of services (QoS) technology as mentioned in this article, how this technology is reducing the operational risks, man power costs, processing costs, help increasing the service based level that leads to higher customer satisfactions and improving the productivity and competitiveness of the network and IP sector. This article discusses the various dimensions of the quality of services (Qos) implementation and its business values, including lowered the operational risks and costs for the organization.
Technical Background on various factors that affect the network performance, especially in dealing with the network that is lacking of quality of service network management and control.
Excessive latency: having excessive lattency in the network can cause voice quality degradation as a result of packet congestions in the network. Different codecs can impact the quality of VoIP and can also add an extra delay on the link. For example, the number of packets that need to be transmitted every second in order to deliver the codec bit rate to a distant end. For example, if G.729 codec with a 20 byte default payload has been used for voice, then 50 packets would need to be transmitted every second to deliver the codec bit rate. Therefore, the loss of a few packets can cause voice clipping and significantly impact the overall voice quality. High, low, or having a lot of variation delay could cause severe impact to the network performance if the application or the network designer had not accounted for these contributing factors when they designed their network. How would this technical term translate to non-technical audiences or high level program manager ?
From the program management perspective, having too much latency causes the quality of service reduces and loss of calls, and unable to allow customers to access the internet while congestions occured in the network as resulted of heavily experienced with too much latency . This would further translated into loss of productivity for a company, degrading network performances and unable to provide the guarantee services to the customers as promised.
In the network, jitter is also a main factor that impacts the voice quality when the buffer is improperly configured in the network set up. If the buffer is too small to accommodate the network jitter, then buffer overflows can occur causing packets to be discarded. The bandwidth consumed per VoIP stream can be determined given the type of codec and sample rate to be used for VoIP. Because of its strict service level requirement, VoIP is well suited for EF PHB, and should be marked to DSCP EF 46. Quality of Service (QoS) can be implemented in various types of network that needs to categorize and control its network traffic. These latency-sensitive, bandwidth-intensive applications add value to company business processes, but the company needs to plan for capabilities and resources to support the implementation and sustainment as part of their life-cycle management and operation. The network designer must take into account the different types of jitter for different types of network they are operating in because the jitter that occurs in terrestrial network that used fiber media can be different from the jitter that happens in the satellite link. In addition, if that information needs to be sent across multiple satellites before it can get to the distant end then there is more differential jitter that needs to be accounted for. Data and data application in general are considered less important than highly sensitive traffic such as voice and video streaming which requires extremely low packet loss to sustain the services. A certain percentage of packet-delay and packet-loss can be tolerated for data transactions. Frame drops occur during congestion. Other traffic without priority assignments shall be placed in a default queue. Traffic in this queue will share the same/equal precedent status and will be provided the best effort delivery.
Network jitter and different classes that QoS offers to improve network efficiency and performances is another techical term which can be interpretted: it’s a measurement factor that measures the network quality, the quality of services, it’s a bad indicator if too much jitter occured in the network. The overall result will put the organization in jeopardy that will be significantly impact their business when they don’t design their network properly.
Keywords: Quality, Performance, Design, Bandwdith, Traffic, Priority, Voice, Sateliltes, Available
When designing and implementing a network infrastructure, poor network design choices may result in less effective quality of services performance guarantees and often leads to significantly loss in profits and productivity. Clearly, network congestion hurts the performance for all users that shares the network together. All network operations have the points where congestion builds and data can be lost that will severely impact the network performance and lost profits. Imagine if the network does not have Quality of Service implementation in place, when somebody is streaming a video, the phone service will suffer and the other applications (web surfing, texting etc…) can’t be used. Because traffic are not classified and prioritized properly so the router is doing its best to share the available bandwidth to all the services but not really considering which one is less important than another. There is no way that we can guarantee the bandwidth when traffic is not marking or allocating to certain users with different levels of priorities. [Figure 1 Network Design without QoS] .
The network operates without quality of service technology could negatively impacts the business operations :
- Provide no guarantee services to customers
- No creditability and less reliability
- No guarantee profits
- Lost to competitors compare to the same services offered in the market
- Deliver Less or no customer satisfactions
- Longer outages and downtime (as it takes time to figure out the problem, fixing the problem and get the network back up)
- More time dwelling into answering phone calls, explaining to the customers
- More complaints from the customer, the key state holder, the shared business (for example, the hospital of MD and university MD campus are sharing the same network so the key stake holders in this case not just from the hospital but also from the key staffs at the university that both sharing the impacts)
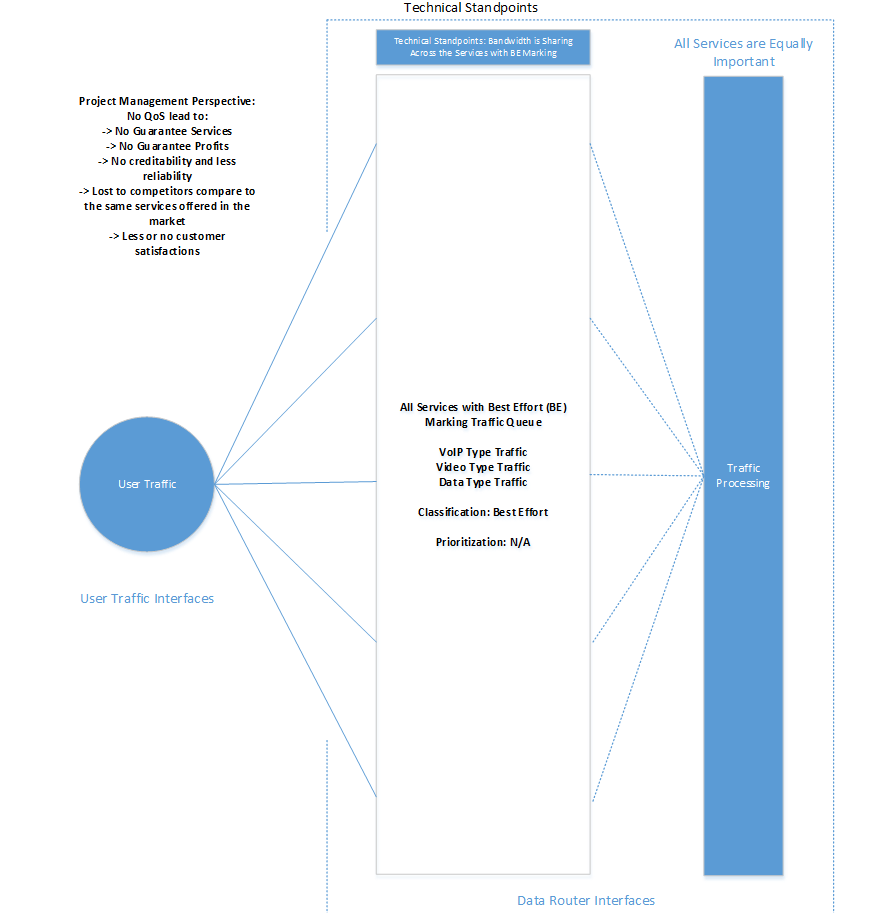
Figure 1. Network Management without QoS from Technical and Program Management Standpoints
All network traffics which includes voice, video, and data that transmitted from the users were routing through the data interface to the router. When the router receives these traffics, it will inspect these packets and make decisions where it would be sending these traffics with the proper level of classification and priority or it just simply flushes them out to the next device if there is no marking identified in the router. In this case, all traffics are sharing with the best effort marking without considering which one is important. There is no guarantee users will get certain services that they should be expected because everybody basically shared the same quality of services. The network will experience congestion and cause packet drops when there are multiple traffics sending from different users.
Proposed Quality of Services (QoS) Approach
The network operates with quality of service technology could positively added tremendous benefits and values to business operations :
- Provide guarantee services to customers
- Increase the company’s reputation, creditability and increase reliability
- Guarantee profits
- Offer reliable and better services to competitors compare to the same services offered in the market
- Increase customer satisfactions
- Attract more business development with different partners (if you network is operating flawlessly with no issues , there is chance that other people would like to do busienss with your company)
- Better reputation, better images to the company, as results increasing in company’s values
- Less or no human intervention, QoS will make smart decision based on different class of traffics
Technical Background on Proposed QoS Network Design Approach:
This section is disucssing about different methods that available in today market to implement QoS into the network to support different traffic classes:
The network device would be designed to accommodate Weight Fair Queuing (WFQ) with the ability to administratively configure the traffic queue. Each queue shall have a different level of priority that can be set up to prioritize traffic based on different type of traffic classifications and different type of services. A percentage of bandwidth shall be allocated to each queue to support these services based on their priority levels. The network device must be designed to support Low Latency Queuing (LLQ) for delay in sensitive traffic. Network device would need to control traffic queues dynamically per flow as desired to ensure fair processing, and prevent the queue from dropping packets when the buffer is overflowed. Flow control techniques should be implemented on the network device, as necessary, to help regulate the traffic, and keep the queue from overflowing on the network device.
IP Type of Services (ToS) uses an eight bits field. The first three bits of the field is the precedence field. This IP precedence value shall prioritize packets within a queue. Packets with a higher priority value will be transmitted before those with lower priorities. The other 5 fields shall be used for network routing and exchange of information (i.e. delay, throughput, reliability, cost and reserved bits). DSCP value is backward compatible with IP ToS, DSCP uses the first 6 bits overlaps with the first 3 bits in ToS. WFQ should be designed appropriately to prevent high bandwidth traffic from overwhelming the resources of a network and shall place the packet belong to each flow.
Proposed Quality of Services (QoS) Model
The high level of complexity in the network that we’re facing today, by implementing the right technology solution such as QoS. The network will have a good control over different type of traffics and be able to assign the bandwidth approriately to different customers and guarantee delivery performances.
This section discusses about how the proposed model would look like to implement in the network in order to have an effective QoS network design:, basically, network desgined with different queue just like a different vehicles on the road. We have the police car, the emergency services, the fire deparment all sharing the same road everyday. These are the people or the services that considered having higher priority and priviledges than a normal car on the road. In the event of emergency, the police can exit the road first to response to the emergency. In similar analogy, the voice service call is conderied as higher priority than the normal traffic such as data, so the voice can transmit first in the network before data can get to transmit.
IP Precedence 6 and 7 are generally reserved for network control traffic such as network routing, broadcast messages, switching protocol, and to keep alive message sending in order to keep the network up and running (References to Traffic Queue # 1 in Figure 1).
There exist two main types of video traffic, interactive-video (i.e. Tandberg, is an example of video teleconference type), and streaming-video using both unicast and multicast. Video streaming is probably more important to us than downloading a big file or surfing the web. The level of priority which should be assign to video shall be higher than that assigned to data (References to Traffic Queue #3 in Figure 1).
Data and data application in general are considered less important than highly sensitive traffics such as voice and video streaming which requires extremely low packet loss to sustain the services. Certain percentage of packet-delay and packet-loss can be tolerated for data transactions. (References to Traffic Queue # 4 in Figure 1).
Other traffic without priority assignments shall be placed in a default queue. Traffic in this queue will share the same/equal precedent status and will be provided the best effort delivery (References to Traffic Queue # 5 in Figure 1).
Even though the IP precedence values 7, 2, 1 are not shown in diagram below, network device shall support these type of services as a place holder in the proposed QoS model.
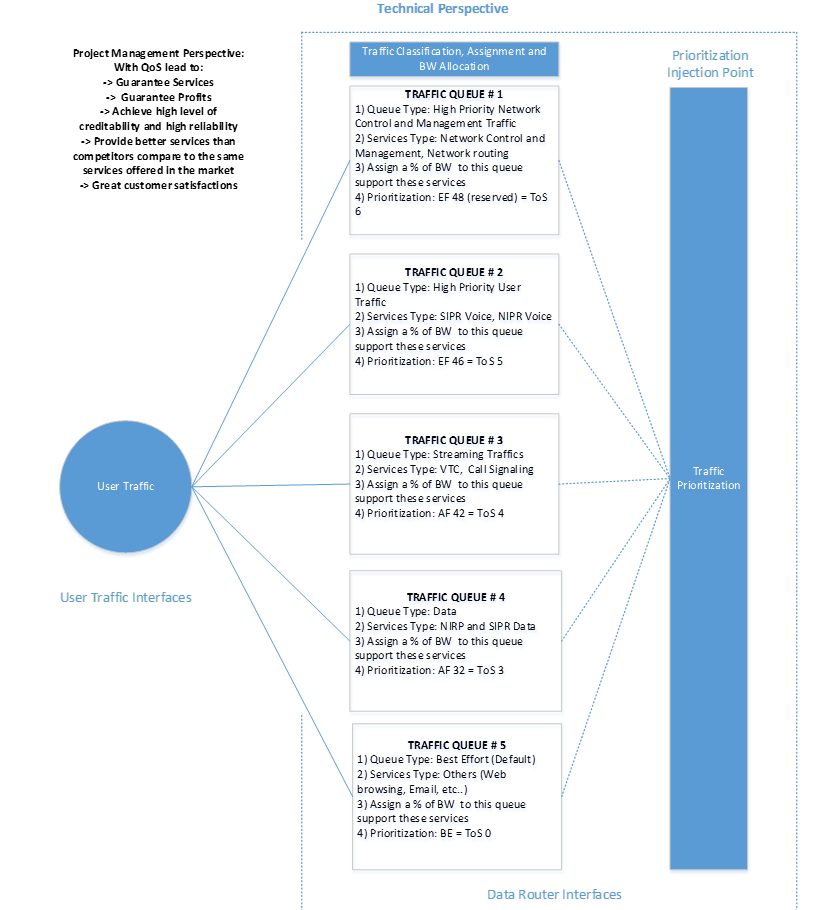
Figure 2. Network Management with Proper QoS Design from the Program Management and Technical Perspective
Operational Risk Management Framework (ORMF) for QoS Technology Enhancement
In business and network design perspective, ORMF is the process of developing the strategy and actions to enhance business performance, minimize loss of profits to increase revenue. Proper network design will provide us with one of the tools to tracking risk, identify new risks, evaluating the performance of the projects throughout the life cycle. We need to analyze the status of the network after the initial deployment, develop the metrics to measure the operation point of the initial investment vs. current ROI. The framework below lays out who’s involved, what’s involved, what network needs to have before deployment. It is an iterative process to constantly assess risk, elevate and resolve the customer issues. The control and monitor loop is the loop between the project manager who is managing the overall of the network performance to ensure the successful of project and program completion. In this case, the overall project manager will monitor, take action to address the issues which related to the network. It is a cost saving solution for the company overall if they considered to implement proper quality of services technology and control in their network. This QoS integration into the network will enhance the productivity, enabling better and faster, reliable communications, guarantee and increase the company’s profit. It also enables customer to improve their overall customer experience with the company for having a guarantee services. Imagine, if the QoS bubble is absence from a below ORMF diagram, then the organization can have tremendous impacts in wrecking with degrading in netwokr performances, lost to competitors, loss of productivity, decrease in customer services, and so on.
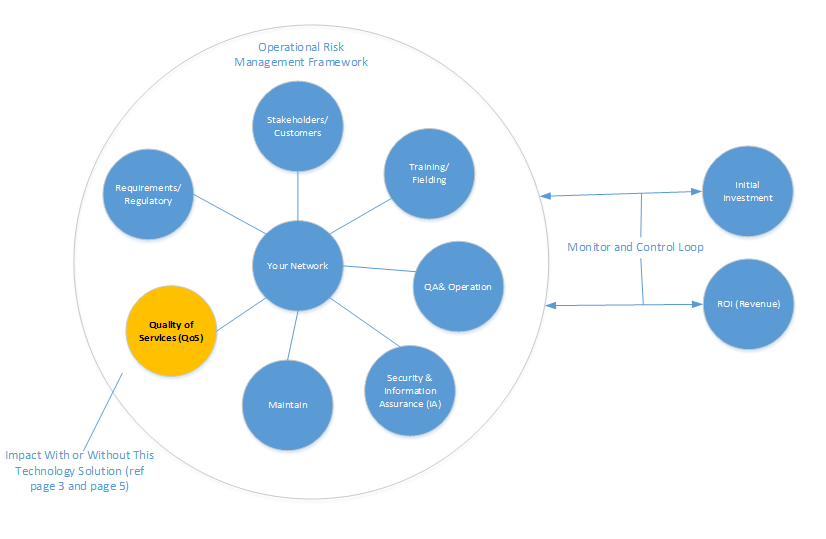
Figure 3. Operation Risk Management Framework
Summary
Whether your network is having problem or not having problem, you must consistently monitor and control it to make sure the performance is expected and customer is satisfied with their services. The dropped calls could result from multiple factors which may happen internally or externally. Let’s say a lacking of QoS implementation may be a contributed factor that could cause the customer dropped calls because all the services are trying their best to share the same bandwidth. The monitor and control loop allows the network manager to prevent network problems to happen, it lets manager know of potential problem before they take action to resolve the issues. The manager must take necessary steps to oversee the operations of the network to manage faults, availability, and performance. It would help them to reduce business risk of downtime and increase network performances. The bottom line if there is problem with the network, a business can lose more than just profit. The article discusses about the QoS technology itself, it lays out the concept of how the network is operating today without the QoS, what is the impact from the business perspective and how would proposed QoS method would help the program manager to increase profits, reliability, and customer satisfactions.
Bibliography:
Kotfila, D. Moorhouse, J. Wolfson, R. (2008). CCNP Optimizing Converged Networks (ONT 642-845) Lab Portfolio. Indianapolis, IN: Cisco Press.
Cravens, D. Lamb, C. Crittenden V. (2002). Strategic Marketing Management Cases 7e. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.