Decision making factors
The question that many network/IT program manager would like to ask themselves is how do we keep our revenue constant? What are some of the things that we can do from the network operation standpoint in order to keep their customer happy and to help increase productivity?
Full title:
Decision making factors: Reducing the risk, opeartion cost, and steps to deploy an effective and redundant network for Network/IT Project Manager
Autor: Minh Nguyen D.
Introduction
The question that many network/IT program manager would like to ask themselves is how do we keep our revenue constant? What are some of the things that we can do from the network operation standpoint in order to keep their customer happy and to help increase productivity? What are the proper steps to design and considered deploying a redundancy network operation? How much effort is needed to restore and restart network to normal operation? How much down time will be incured , and how much would it cost to get the network running? What are some of the hiddlen costs that may be encountered that not in the planning? The artciles is written to help answering some of the questions below:
- Ping point what some of the things could go wrong with the network when they are not designed with redundant component
- Steps to plan a redundant network
- Decision making factors weigthed benefits factors vs concerns factors
Background
Whether the business opeation is considerd simple and small network deployed for a small office or multiple networks deployed across multiple campuses. One of the way to reduce downtime and minimize risk to provide continuous operation is to ensure the network is designed with a back up solution. Today’s enterprise and mobile networks are so powerful that they are often very difficult to manage because organizations whose operations are highly dispersed around the globe and their networks are increasingly large with high scalability. A large network can have thousands of computing platforms around the globe which operate on different infrastructures to support many customers. Networks should be designed with zero fault tolerance to keep customer satisfied. Network should be designed with primary connection and backup connection to minimize the downtime and cost. The design of the network whether a local area network (LAN) or wide area network (WAN) must have the need for a backup to take over in case of any type of failure to the main link.. A simple example would be if you had just a single connection in your network that connects your home to the Internet Service Provider (ISP). What if that link went down and never comes back up in a short amount of time? How would you continue your operations if it did? In this article we will discuss some of the design and plan for a backup solution that someone can count on and one that is cost effective and affordable to operate. To keep the business operational at all times and to increase customer satisfactions, as mentioned earlier, we as the program manager, network planner must implement the back up network solution so the network will have a standby link to backup the primary link when the main link of the network goes down.
Some company don’t want to implement the redundancy operation is not because they can not afford it but because they lack an understanding of the severitiy and criticality of the network requirement to provide the redundancy operation. They don’t think it’s a big deal when the network goes down, they thought it can be a simple fix with hiring some smart people to restore the network easily. In this article, we’re trying to propose an approach to help program manager to implement the right solution to keep their profit constant and prevent their network from failures. Network redundancy will help the small business, program manager, network planner to reduce risk and minizmie the down time and improve customer satisfactions. The bottom line is we never want to design a network as a single point of failure that we have to rely for it to come back.
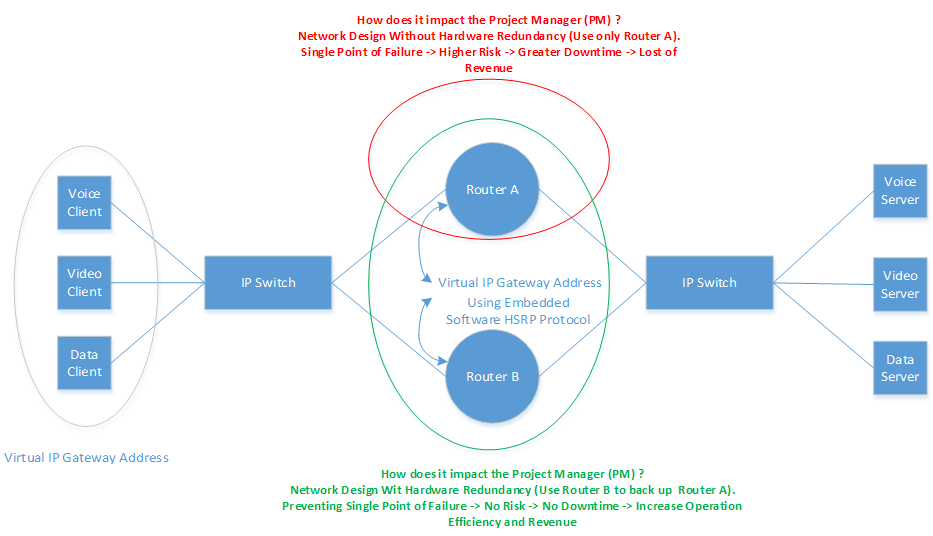
Figure 1. Hot Standby Router Protocol Network Redundancy Operational Diagram
Project Managemnet Man Power Cost ($) Incurred in Practical Scenario without Rundancy:
Design a network without considering implement a redundancy option could be a high risk for the organization, especially, when dealing with the equipment failures in the network operation. Figure 1 illustrated a scenario that network was implemented without a hardware redundancy when one router (Router A as depicted in the red circle) only used in the network. When the outage occurs , and no back up solution in place to kept the operation running , it will result in greater risk and lost of revenue to program manager.
When router A is stopped working and no backup solution (identifed as router B) has been planned . The company would have to send somebody in to troubleshoot the network and restore the network to the normal operation. Let’s say, the cost of average network engineer earned around $70/hour. Depend on how simple or complex of the problem that needs to be repaired, let’s say the problem requires 2 full days of work (48 hours) to restore and repair the network. Therefore, the cost that company must spend to fix the problem within two days is ($70/hour x 48 = $3360 per 2 days). The cost could be higher depends on how small or big of the job that needs to be involved. This is just an example how network redundancy is important to assit the opeation and help saving cost for the company.
Project Managemnet Man Power Cost ($) could be prevented with implementing the hardware redundancy:
To stop being a single point of failure in the network operation. Back up solution must be identified in advances when the designer considers the network implementaiton. In this case, designer will have to implement two routers in the network , with one is being used to back up another in case of outages occur. Figure 1 illustrated a scenario that network was implemented witth a hardware redundancy with using two routers (Router B is used to back up Router A as depicted in the green circle). User should not be worry about the outage because Router B will immediately take over the ntework when the Router A goes down. The transition from Router A to Router B should be transparent to the user. Program Manager is expected no outages or downtime in the operation and kept generating the constant profit.
Keywords: Redundancy, Operations, Network, Bandwidth, Hardware, Software, Standby, Virtual, Router
Network Redundancy with Hot Standby Router Protocol Best Practices
Enabling network redundancy using the Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) to provide redundant router services to the network systems involves three major components: the router hardware, the router software, the web router to act as web server, and the workstation to act as end user client, and the configuration backup system. The objective is to be able to switch to a standby link as quickly as possible in the event of the primary link outage. The software runs on the router will make intelligent decisions when to switch to the standby link. We need two routers as the minimum to set up the network with HSRP. Two routers A and B are connected to your network. Using the two default gateways from router A and B does not provide a reliable path in the event of an outage. HSRP is implemented on your two routers through using a virtual IP gateway address that provides a fast failover mechanism that is transparent to the users. This allows hosts on the LAN segment such as voice client, video client, and the data client to maintain access to the web router in the event of a router failure. HSRP lets you create the virtual IP address that floats between the routers, in the event of the primary router fails. The default priority is 100 for all routers. So, let’s say that you have two routers A and B in your network. You make the router A the active HSRP router by setting the priority to 200.The preempt command will allow a router with the highest priority to take over as the active HSRP router. The fundamental of HSRP will be depicted in a diagram. HSRP provides fast failover devices on a LAN segment containing two more Cisco routers. If both of the routers went bad, then we would need to replace the defective hardware with a good working hardware before we attempt to bring up the network again. For software failures on one router, the second router can act as a backup. The data and router configuration must backup to the server and keep in the database whenever it needs it. The basic principles are the same to implement HSRP in the larger network vs small network. Fewer routers will be needed when implement HSRP in the small networks compare to large network. Our goal is trying to reduce downtime, and getting the network restores as quickly as we can to the point as seamless that users do not even notice there was an outage. We would have to make a trade off in the design when we choose which hardware to use in the network. The more expensive hardware is faster and performs better than a cheaper hardware.
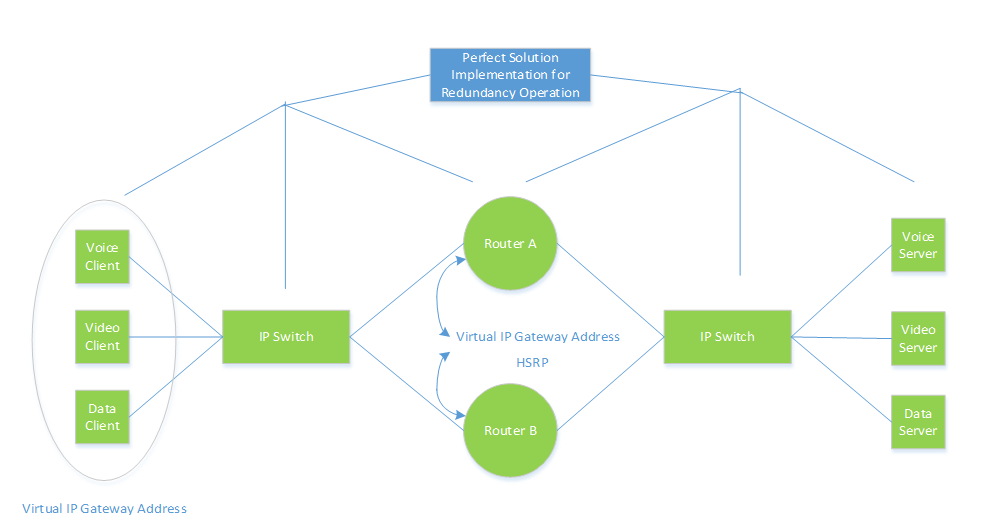
Figure 2. Hot Standby Router Protocol Network Redundancy Designing Considerations Diagram. (Green represents the redundant hardware/software and Blue represents the redundant for connections)
Perfect Solution Managemnet Approach in Dealing with Network Redundancy In Operation:
When designing a network, the designer should always consider having some redundant components in the network such as redundant hardware, software, cables, power, fan, and a contingency plan to execute in the event the primary plan fails.The point to emphasize here is redundancy is not always happening at the core component in the network such as (Router A and Router B solution as identified in Figure 1). To carry out a perfect solution and to have a piece of mind solution , the program manager must considers to provide the component redundnacy across the board in the network. The Figure 2 illustrated the injection point for hardware redundancy consideration in the network. For servers and network devices, redundant hot-swappable power supplies and drives (as well as other components) are used to keep everything up and running when a disaster occurs. If the drives of the server fail, the data is not lost if it got saved to the other drive. Anytime we incurred the lost of data, services, memory that results negatively impact to the total revenue , so the program manger’s responsibility is taking all the pre-caution as nencessary to prevent them from happening. In the example above, the Hot Standby Routing Protocol (HSRP) is the software based which resides on the router that makes a smart decision when it needs to switch to a backup link in the event the primary link fails. In the event the hardware fails on both routers then there is nothing we can do to make HSRP work without replacing to the new hardware. Therefore, operating with redundant hardware is critical to keep the business up and running all time with minimal downtime. The longer the downtime it has, the more lost to the business and the less satisfaction to the customers. As the manager of the network operation, they’d like to see data is saved in multiple locations to provide fast restoration and redundancy options. In a Figure 2 above, those components that are in green color represent the components which are required having the ability to perform the primary and backup functions. We need to plan our network to have redundant components such as the video, data, and voice client and servers must have a backup hardware and software which is identified in the contingency plan. Same as the routers, the blue color represents the inter-connection between the client and servers through the IP switch and the routers. These cables also need to be saved just in case we have some kind of major failure with a cable we can quickly switch off to a different cable. If you need to support a new requirement at higher speed that needs to open a new connection, you will have that option without buying and installing new cables as it is very expensive to go back and add new cables later. This will lead to less downtime and more efficient operation even though it costs a little more upfront in our initial investment for designing a network.
Project Managemnet Man power and Equipment Cost ($) Example in Practical Scenario without Redundancy:
When router A is stopped working and no backup solution (identifed as router B) has been planned . The company would have to send somebody in to troubleshoot the network and restore the network to the normal operation. Let’s say, the cost of average network engineer earned around $70/hour. Depend on how simple or complex of the problem that needs to be repaired, let’s say the problem requires 2 full days of work (48 hours) to restore and repair the network. The total cost is estimated to repair this issue in previsous scenario is 3360 for 2 days of repair. However, what happens if the equipment is not available at the time the engineer shows up on site for repairing or the equipment did not arrive as expected due to lost of packages, packages sent to wrong receiver, delay in shipping and receiving due to inavailability of transportation. In this case, let’s say the company would have to incur more costs in proceeding the alternative solution by purchasing the router from a local store while waiting on the online shipping arrives. The cost of the online router is $5000 vs the cost of the router which purchased locally is $7000. The difference that compnay would have to pay is $2000. Asssuming, it’s still taking two days to repair the network, plus the increase in equipment fees due to not receive the equipment on time. Therefore the total cost of repairing the network which includes purchasing the local router is 3360 + $2000=$5360).
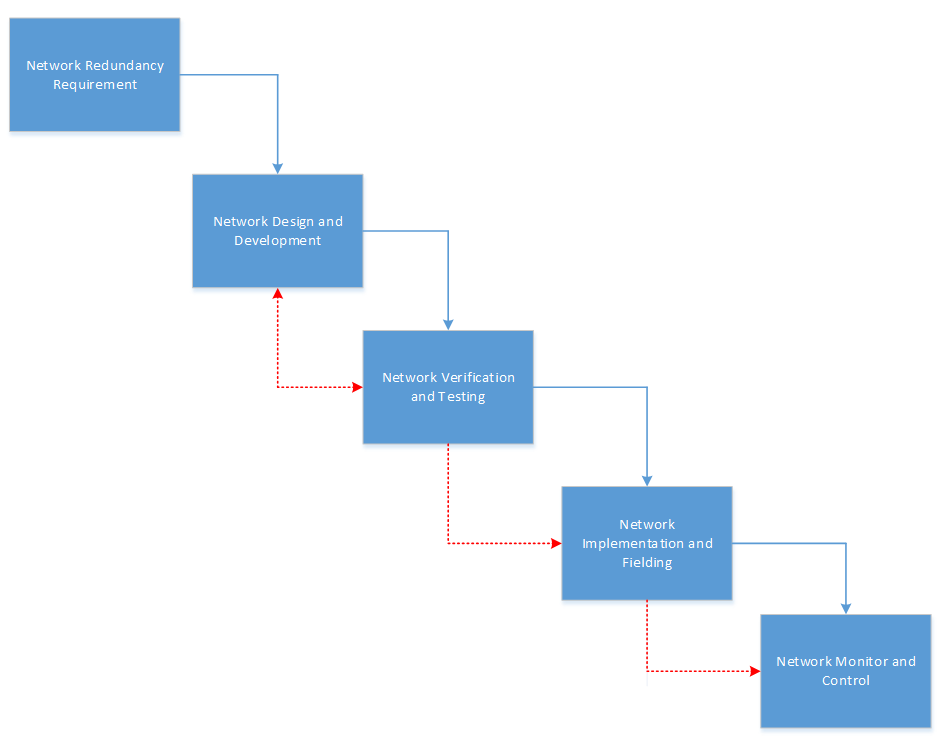
Figure 3. Steps to Deploy an Effective Redundant Network for Project Manager/IT Manager
Certain methodologies to deploy a redundant network may be more suited for one network than another. These steps provide the standards-based redundancy methodogies framework to deploy an effective and redundant network to avoid outages. To satisfy our customers, a business or company network must be reliable at all times. The network shall be designed with redundant hardware and software to protect against unexpected failures and keep the network operation at zero tolerance. The network must also be able to adjust to adapt a new demand quickly to maintain consistent and resolve issues in timely manner. As part of network redundancy requirement check list, we need to understand the business goals and technical requirements, conduct surveys and decide what functions are required to satisfy customer needs, create a project plan and a backup plan before moving to the next development and design phase. Some of the common requirements for designing a network such as (high availability, security, customer services response in timely manner when failures occur, redundancy operation, scalable design based on the size of network). In the next design and development phase, we need to understand the existing operating infrastructure of the network then gathering the data and analyzing the result of the collected data. Determine whether if anything can be re-used, any new equipment, functions that need to be re-designed, security also plays a big role in designing a new network infrastructure. Determine any new regulatory requirements we might have to adapt to when design a new network. We need to meet with the manager and the customer to ensure the network design solution is sufficient to support the customer requirement. In the next phase, we have to do a proof of concept by verifying and testing our designed solution to ensure it works as we expected. This approach ensures that new design functions as expected before it is implemented. Some of the fundamental designed factors such as: improve network efficiency, using highly qualified hardware and software with high mean time failure repair for the equipment’s, adding new cyber security to the network, backup data in multiple locations to save data so it will not be lost, redundant components increase cost, but they are usually well worth in our initial investment, should the network be designed with hot standby, hot swappable options, using interruptible power supply (UPS) to backup power and having system running dual fans, design a security policy. After the network has proven in the initial proof of concept, it is ready to move on the next phase. The next step would be implementing and fielding the network design concept to the customers. We have to consider whether we need to ship this equipment out to perform the installation on site, if so, we have to plan in our schedule the time it takes for shipping the equipment, the time to get to the site and perform the installation to the equipment. Factory acceptance test is one of the critical tests to verify to make sure the network is working when it is installed at the customer site. The customer must sign off on these testing before they accepted the product. The vendor performs the test and customer witness and sign off on the test. Any issues must be resolved onsite before customer sign off the acceptant testing. The final step/phase is monitor and controls the network. We need to follow our security policy, disaster recovery plan to response to incident if it happens, take necessary actions to resolve the issues when customers have problems. There are issues that may not be repairable right away, or resolvable without the expert or proper equipment on site. We need an after action report where you can specify how things will be fixed, and resolved. We also need to do analysis, assess risk and take proper action to address the issues. Analyze why the main connection terminate? Can we turn on the backup without impacting other services? What type of routing can we modify?
Conclusion:
The article presents some of things that could go wrong in your network such as failure of the hardware, physical cabling sytsems, wires, etc.. and the associated impacts of the downtime and the injection point where redundant component could have been designed to protect the network. From the IT or network program manager pespective, we need to understand the cost of the downtime that significantly impact the business financially such as results of the loss of productivity and creditibaility to the competitors, deceasing the efficiency in the network operation. IT and Network program manager need to consider steps as precaution to put measures in place to protect from these losses and mitigate risk. Some of the weighted factors as identified that lay out the benefits and drawbacks when they considers making these decisions and investment in their network.
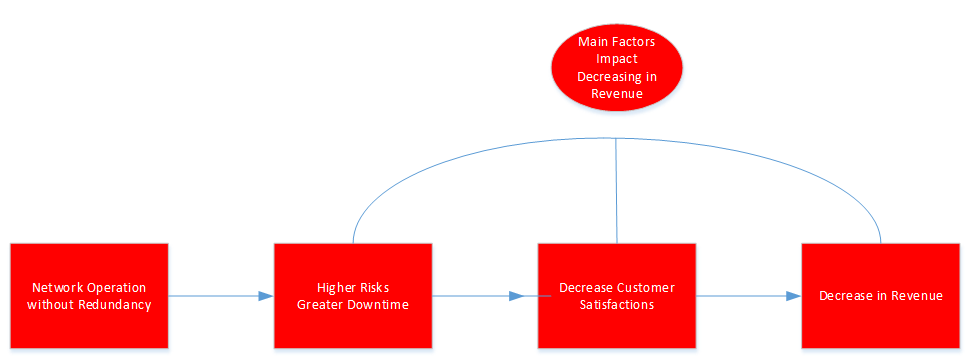
Figure 4. Manager Considerations and Decision-Making that Impacts the Revenue without the Redundancy
What are the drawbacks or concerns for not considering the redundant network operations:
- Less reliability, slow failure recovery (for example, how soon can you get the network technican on board to fix the problem, how many of them do we need, how many days do they take to fix the network, whether the equipments are available for installing?)
- More outages, more downtime, (as results customer may be decided to switch to differnt service provider to get a better services)
- Damages to the equipments ( if the equipments don’t get to swap out in time, the equipments might get damanged and more moeny would have to spend to fix that hardware before it can put in service again).
- Could lead to saftey concerns for the company if the failures equipment dont get to replace in time, active components may generated more heat, air ventilation may get blocked and created a lot of risks to damange other equipments in the same location.
- Loss of productivity, for example, resources are off line, staffs are standby waiting for network to restore, it could be a major concerns in potential significant financial impact
- Results of lost to competitors ( let’s say network provider A provides 99% uptime vs provider B which is your network only provided 75% uptime) . In this case, customer would prefer to use network A over your network B.
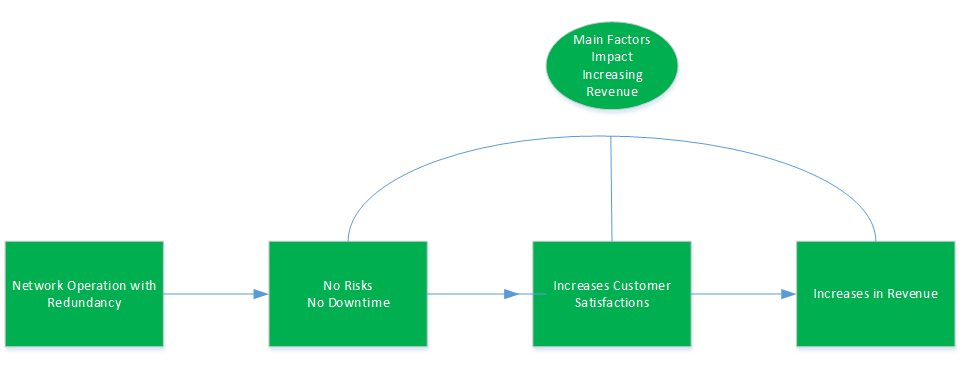
Figure 5. Manager Considerations and Decision-Making that Impacts the Revenue with the Redundancy
What are some of the benefits / values to create a redundant network operation:
- Little to no maintenance of the network
- Less manpower or staffs required to monitor and control the network
- Reduce operational risk by switching to standby hardwarre in the event of the failure of the primary hardares
- Fast recovery times, stabilize the network and operation peformances
- No damanges to hardares
- Increase network performance, management, productivity and reliability
- Less security concerns to the network infrastructure
- Better Return on Investment, the cost of downtime vs the cost of redundant system. For example, 3360 dollars for 2 days the money that need to spend to get the network fixed vs the cost of the router let’s say the cost to implement a redundant router is 5000 dollars. The Return on Investment (ROI) can be calculated (5000/3600=1.38 days). In this situation, it takes approximately 1.38 days to recover from the cost of implementing the redundnat operation vs no redundant implement in the network.
As we understand, then network redundancy solution is not only helping the IT/Network program manager to minize the risk of the network downtime and maximize the uptimes, but it also provides the stability and opertional performancess to keep the customer happy. Thinking from a standpoing, when the customer would have to make their decision to switch to a different network provider because they could nto afford to sit there for long hours to wait for the network work back up so they could do their job. As the IT/ Network program manager we need to make a smart decision whether it is a well worthed investment to put in a redundancy solution in their network to prevent the mission critical applications and high availability mission from failure. Considering design an optimum network is critical to success and putting the right solution in place to create a network with high availability and offers reliable services to our customer will help the business cutting down the cost, increase customer satisfactions, and improve operation. In this article, we suggest the paradigm to design an effective and redundant network, how to design, implement, monitor and control the network to satisfy the customer needs and how to prevent failures in case disaster may occur. The artcile ping point the area that the IT/Network program manager would consider to prevent the network from failure such as failures could occur anywhere in the network infrastructure like physical wire, cables, conduit, routers hardware, software, switches in order to maintain the continuous opeation. The interuption to the network that might imapct more than just the services that provided to customer, but may lead to equipment damanges, safety of the infrastructure.
Bibliography:
Kotfila, D. Moorhouse, J. Wolfson, R. (2008). CCNP Implementing Secured Converged WANs (ISCW 642-825) lab portfolio. Indianapolis, IN: Cisco Press.
Hitt, M. Duane, I. Hoskisson R. (2005). Strategic Management: Competitiveness and Globalization (Concepts and Cases) 6e. Mason, OH: Thomson South-Western.