A Research On The Application Of Strategic Management Tools And Techniques In the Singaporean Companies
Massive changes in the economic environment, as well as the tide of globalization, are pressuring businesses to establish management strategies geared at boosting worldwide competition. Organizations' business environments are rapidly changing. Singaporean businesses confine themselves to creating a management strategy geared at rising worldwide competitiveness, especially with the rise of e-commerce and the globalization of creativity. CRM (Consumer Relationship Management) was determined to be the most extensively utilized technique among the 25 tools and approaches studied, followed by benchmarking and staff retention surveys. Depending on the specialization, the number of strategic management tools and approaches employed as a study topic varies.
Introduction:
The business environment of organizations is evolving rapidly. Particularly with the expansion of e-commerce and the globalization of creation, Singaporean organizations limit themselves to planning a management strategy aimed at increasing international competition. Moreover, there are constant innovations such as IoT, AI, and robots, so the development of new products and new business areas with these advancements has become important for companies (Song, Yang, Huang & Huang, 2019). Was the leading figure to characterize techniques in school management. He characterized the strategy as "ensuring the fundamental long-term goals and objectives of a company, as well as selecting building plans and allocating strategic resources to achieve those goals."
The characterized strategy as the example of goals, objectives, or goals and the guidelines and reasonable plans for achieving those goals, expressed to characterize in what company the organization is or will be and in what kind of organization it is or will be. We can understand that the technology was what companies hoped to help them achieve future goals, because of rapid e-commerce development creating problems (Babenko, Kulczyk, Perevosova, Syniavska & Davydova, 2019). The best-known importance of business strategy in business art today is that of Michael E. Watchman from Harvard Business College, who was also named "The World's Leading Business Thinker". Consciously choose an alternative set of exercises to provide a unique combination of significant value.
This perspective emphasizes the spread and value of your own organization as opposed to different organizations. With this in mind, he developed Value Chain Inquiry and Porter 5 Authority Inquiry. Likewise, found it necessary to consider future headlines as well as natural changes over time and characterized the strategy in five types: "plan, plan, pattern, position, perspective". On the other hand, the Resource-Based View (RBV) strategy characterized the strategy as "an example of the allocation of resources that companies can use to track or improve their performance" (Arbelo, Arbelo-Pérez & Pérez-Gómez, 2021). In this sense, although different researchers have given the strategy different meanings, there is still no global and uniform definition (Chuang & Lin, 2017). Composing the meaning of technology would be problematic, but "achieving goals and objectives" is a typical part of many definitions. In this sense, technology is characterized in this thesis as "the strategic strategy of an organization for achieving goals and objectives in an evolving environment".
According to (Hassink, Isaksen & Trippl, 2019), strategic management means a broader concept than technology and is an interaction where top management studies the environment in which the organization operates before planning a strategy, as well as the schedule of performance and control of the strategy. It's been over 50 years since it first appeared. During this time, various strategic management tools and techniques were developed (Berisha Qehaja, Kutllovci & Shiroka Pula, 2017). There are different emotions regarding the importance of strategic tools and strategies. But if we follow Windschitl, Thompson & Braaten (2020), it can very well be said, "The strategy tool is used to involve the full range of ideas, thoughts, strategies, and approaches that are strategic thinking, dynamic and technical of the movement. Do organizations need to use these tools and strategies for dynamic management techniques - monitor usage frequency across business types and assess the impact on business performance while monitoring issues.
Literature Review:
Strategic management tools and techniques are also referred to as "strategic (planning) tools or potential methods", "additional strategies and management tools", "additional business tools and methods", "additional strategic research tools and methods" or "Strategic Toolboxes” (Gallo, Mihalčová, Gallo Jr, Čabinová & Tomčíková, 2019). While these terms and content have some contrast, all professionals use them equally to adapt to the objectives of the study. In this sense, the associated academic definitions, including the meaning of "strategy", have not actually been established (hereinafter referred to as "strategic management tools and methods"). All the terms are used together in every way to provide tools and strategies useful for the various management dynamics along the way to strategic planning and execution. Using 11 measures (time, cost, management skills, utility, constraints and the others) examined the 21 available tools and methods that managers use to specify management strategy (such as political and national risk research, BCG industry network, critical performance factors, value chain research) and presented the results. Evaluated 30 tools and strategies that would be needed in formulating strategic management guidelines and assessed whether they were useful for the strategic dynamics of managers and professionals. Madsen et al. (2019), researched the consulting firm, Bain and Company, have continuously researched the use of management tools by managers in organizations around the world, and have conducted public surveys since 1993. As of 2015, there were 13,000 respondents from more than 70 countries in North America, Europe, Asia, Africa, the Middle East, and Latin America. (Fifteenth overview).
This study found that of the 25 tools and methods used worldwide, the most widely used tool was CRM (Consumer Relationship Management), followed by benchmarking and then employee retention surveys (Guerola-Navarro, Oltra-Badenes, Gil-Gomez & Gil-Gomez, 2021). In addition, it shows (1) that there are different positions for each tool and technique in the sequential requirement, and (2) that each area had different positions (the most commonly used tools and strategies were CRM and benchmarking in the EMEA Local Area CRM (customer relationship management) in the North American district, strategic planning in the Latin American region, and big data analytics in the APAC area (Rigby and Bilodeau, 2015). methods completed in agricultural countries.
Choudhary, Nayak, Dora, Mishra & Ghadge (2019), found that the tools most commonly used in manufacturing and medium and private companies in the UK support activities were business analysis, SWOT research, and strategic skills (GURL, 2017) examined the conditions of 14 strategic planning tools and methods used in modern economic, administrative and administrative organizations in Jordan and assumed that the most commonly used strategy was economic research. Subsequently, PEST study, Porter's 5 Forces study, strategic (core) performance factors analysis, Core Skill / Fitness study, SWOT study, etc. were conducted. in different parts of Turstrategic, the city of Antalya. The results showed that strategic planning, personnel research, TQM, CRM, and financial research were used from time to time.
Jovanović, Dražić-Lutilsky & Vašiček (2019) assessed the use of 25 governance tools in organizations in Slovenia and Croatia. The most commonly used sliding application tools in Slovenia were reassessment, benchmarking, core competencies, knowledge management, and general quality management. In Croatia, however, these were mission and vision, benchmarking, core competencies, customer relationship management, and customer segmentation. While practically comparative, it shows that there are contrasts, especially between the most commonly used tools. In addition, Pu, Teresiene, Pieczulis, Kong & Yue (2021) examined the number of Lithuanian supervisors using the 12 strategic management tools in business practice and found how many managers use SWOT research. Despite the country-specific reviews, Runge et al. (2020) have conducted research around the world, targeting different countries. The authors considered and examined these four studies. He found that the SWOT study and benchmarking in three of the studies played an important role in the most commonly used strategic management tools and methods (Berisha Qehaja, Kutllovci & Shiroka Pula, 2017). For the strategic management of leaders, the tools and strategies and innovation, as well as the repetition of the implementation, are not only contrasting for each area but also depend on all countries (Demir, 2018).
Berisha Qehaja, Kutllovci & Shiroka Pula (2017) cited an international correlation between the use of 66 strategic management tools between the UK and New Zealand, distinguishing the contrasts between them and the organizations discovered, which typically used 33 tools, which accounted for half the tools. In addition, analyzing the use of strategic instruments in Australia, Singapore, Hong Kong, and Malaysia in the context of research. examined the use of strategic management tools and strategies for SMEs in Finland and Russia and found that benchmarking was most common in Finland, and outsourcing was most common in Russia, and there were strong contrasts in the rate of use. Vaitkevičius (2007) discovered the consequences of a study of the knowledge and possible use of management tools for managers in production, retail, discount, and management companies in Lithuania.

Vaitkevičius’s Mission, strategic objectives, vision, strategic alternatives, leadership structure, SWOT analysis, Porter's Five Forces model, PEST research, product portfolio matrix, DELFI technique, management style, and scenario model were among the tools and methods employed. In addition, some important studies have been conducted to explain the correct relationship between strategic tools and management performance. This is significant research from the perspective of flexibility from hypothesis to experiment (Chou, Chen & Kuo, 2018). However, the use of strategic management tools and strategies has not been shown to positively impact organizational or financial performance in all studies. Overall results, such as tools and methods that are regularly used, could not be achieved under the guidance of analysts who differ from country to country due to the nature of the company, corporate culture, business environment, and management style (Qehaja et al. 2017). In addition, there is the problem that basic research is difficult to implement because the number of strategic management tools and strategies concentrated by analysts is unique.
Hypotheses:
H1: In Singaporean organizations, the utilization pace of strategic management tools and strategies is diverse relying upon the business type. (In the manufacturing enterprises the use rate is higher than in the retail business and more tools are utilized.)
H2: In Singaporean organizations, if the organization utilizes a higher number of instruments, organizational performance is higher.
H3: When managers have a profound premium in management technique instruments, it affects organization performance
H4: The more managers emphatically perceive the effectiveness of management strategy tools, the higher the organizational performance.
Research Methodology:
In previous studies, the number of strategic management tools and methods used as a research topic varies depending on the specialist. In this study, we selected mainstream tools and methodologies and added KAIZEN, ISO9001, and BCP (Business Continuity Plan) tools that are believed to be widely used in Singapore (Păvălașcu & Gabor, 2020). KAIZEN is a management tool that can test the top management of an organization with specialists, and it is a Singaporean term meaning "continuous improvement" or "continuous improvement" (Hosono, 2020). In Singapore, its use is necessary not only to spread to manufacturing companies, such as Toyota's auto organization but also to various companies. This is believed to be one of the reasons for Singapore's management success, which focuses on products and management quality (Quah, 2018).
Likewise, ISO9001 is a standard that recognizes that a specific standard for products and management quality has been met and that more than 1,000,000 have been earned worldwide. By all reports, it is widespread, especially given that Singaporean organizations dealing with Western countries have been focusing on it for a while. In addition, the need for BCP planning in Singaporean organizations has increased since the 2011 earthquake in Singapore's Great East, and courses have been held across Singapore (Anbumozhi & Kimura, 2020). We chose this because Singapore is in shock and that is why many organizations seem to be adopting the BCP. Finally, 26 strategic management tools and strategies were selected. These were benchmarking, SWOT research, situation research, piece-by-piece research, PEST research, strategic performance factors (core), 5 porter powers, mission and vision announcement, PPM (product portfolio management), Ansoff framework, VRIO Research, strategy material, ISO9001, TQM (Total Quality Management), Inventory Management Network Management, KAIZEN, Representative Fulfillment Management, Customer Loyalty Research, Advertising Mix (4p), STP Research, CRM (Customer Relationship Management), Information Management, Value Chain Management, Economic Research, Balance Scorecard, BCP.
The performance of an organization is characterized by "a set of economic and non-financial indicators that provide data on the extent to which goals and results have been achieved" by Kumar & Ganguly (2020). In this study, the five appendices are used as the organization's performance file. For each question, a self-perceived 5-point Likert scale from 1 (clearly different) to 5 (strongly agree) is used, and the absolute value is used as the target variable.
(1) Financial indicator for organizational performance
- Revenues and consumption in the past three years (propensity for profitability)
- Profit gain from transactions is greater than normal.
(2) Non-economic indicator for organizational performance. of a new product,
- improvements are higher than in several organizations incomparable industry revenue.
- The turnover of ordinary employees is below the normal value of the company.
Results and Discussion:
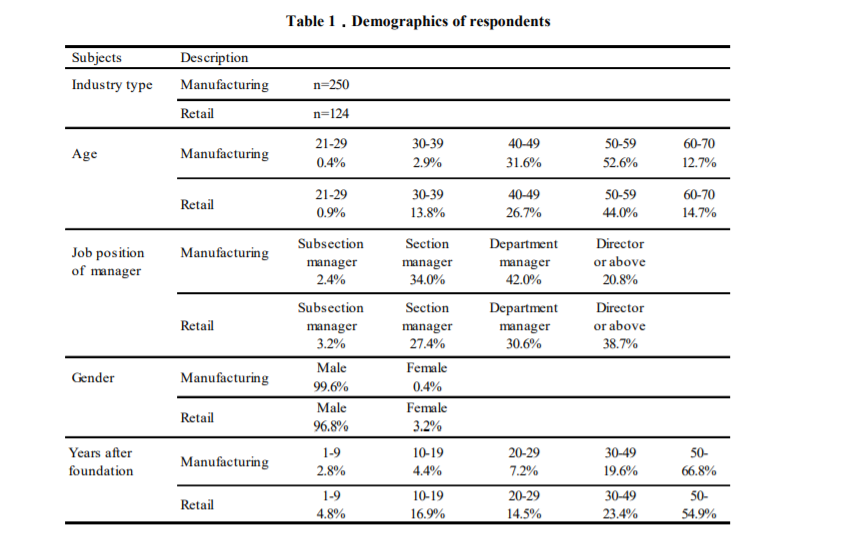
Table: Demographics of Respondents
Source: Self-Designed
In terms of respondent characteristics (see Table 1), the primary age group in manufacturing and retail companies was 40 and 50, and this age is also innovative in determining management strategy. In terms of functions in both production and retail, within the managers, there were many functions above the segment manager, but not many sub-department managers. Most of the leaders were also men. In terms of the age of the organizations, most organizations were founded only 50 years ago. Not many youth organizations were established less than 10 years ago.
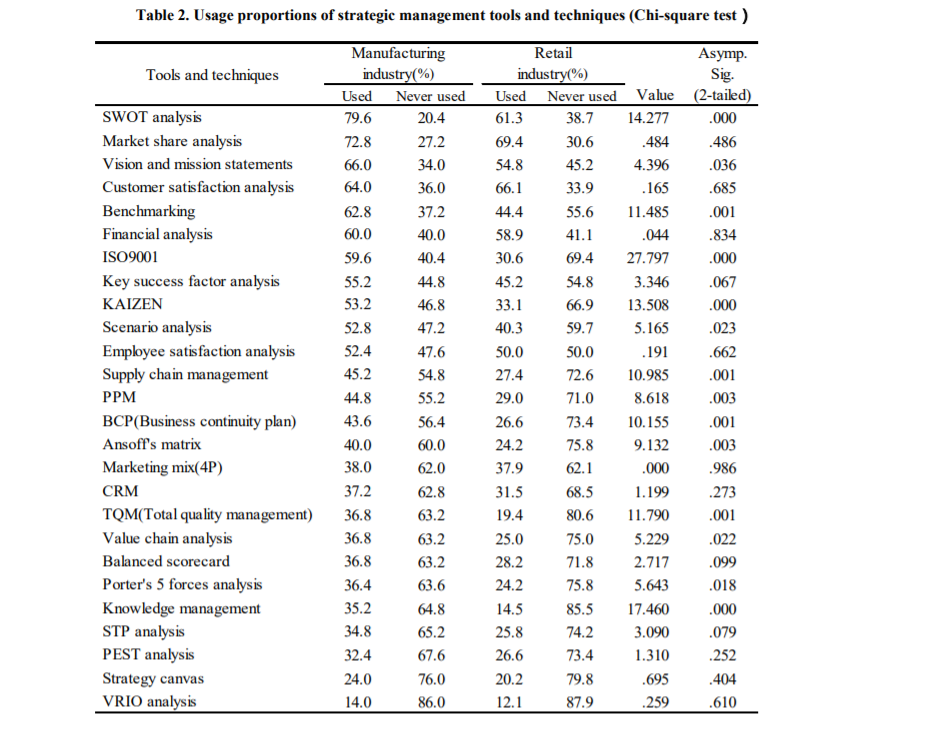
Table: Usage proportion of strategic management tools and techniques
Source: Self-designed
As indicated in Table 2, the rate of use of strategic management tools and strategies in manufacturing is generally higher than in retail. In manufacturing, SWOT research (79.6%) shows the most notable rate, which is higher than that of retail (61.3%). This can be measured very well at 0.1%. The SWOT research was a technique that was developed and introduced in the 1960s and distinguishes the qualities, defects, openings, and risks in a 2x2 grid (). This can basically be examined for both the internal environment of organizations and the external environment of organizations, and the term is simple. Against this background, the supervisory authorities can detail suitable strategies.
The second-highest usage rate of tools and techniques for market research is market share research and customer compliance research. The 5% distinction between manufacturing and retail is not fundamental. The vision and mission joints have a high utilization rate abroad and are tools with a high utilization rate. They rank third (66.0 %) in manufacturing and fifth (54.8 %) in retail, including organizations in Singapore. Benchmarking has a high usage rate in the manufacturing business, which is a stark contrast to the retail business. Economic research is a tool that is used in a large part of the size of organizations in the two companies. This implies that it is imperative to examine the circumstances of transactions, payments, and ownership with little consideration of the line of business. KAIZEN and ISO9001, which seem to be well known in Singapore, have a high utilization rate in the manufacturing business and are used by more than part of the companies, however, the utilization rate in retail is strategically lower….
Table: Mean number of strategic management tools and techniques used
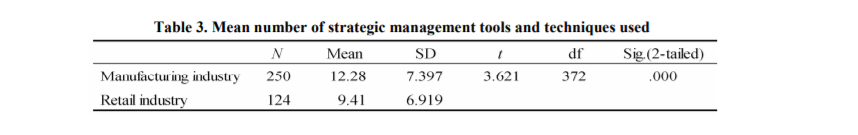
Source: Self-designed
Apart from that, the tools are statistically significant at the 5% level: situation survey, network administration, PPM, BCP (Business Progression Plan), Ansoff framework, TQM, value chain, Porter's 5 power research, and knowledge administration. In more than half (14) of the 26 tools and techniques examined, it is really huge at 5%, and in each of them, the utilization rate of the production store was higher than that of the store. In addition, there is a very critical distinction between the average number of strategic management tools and strategies used. Production is 12.3 and retail is 9.4 (see Table 3). Hypothesis 1 is supported by the above. The three instruments with the lowest application rate were VRIO research, strategy material, PEST research in production and VRIO research, knowledge administration, and TQM in retail. VRIO's survey had the lowest occupancy rate in both companies.
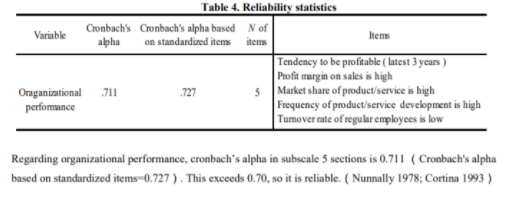
Table: Table 4
Source: Self-designed
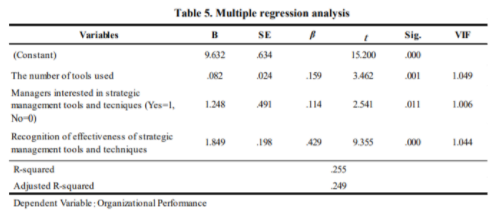
Table: Table 5
Source: Self-designed
To test hypotheses 2 to 4, multiple regression research was performed that covered organizational performance for the dependent variable (see Table 4). Any variation in the expansion factor (VIF) of the autonomous factors is less than 2.0, so that the problem of multicollinearity tends not to exist. The consequence of this regression research showed that the three free factors accounted for 24.9% of the difference in organizational performance (F = 42.149, p <0.001). The implications of this research indicate that the use of strategic management tools and strategies affects organizational performance. In addition, the manager's premium for strategic management tools and methods has an impact on organizational performance. In addition, a strong sense of the appropriateness of strategic management tools and strategies by the manager has been found to have an impact on organizational performance. The more managers perceive the appropriateness of the management strategy tool, the higher the organizational performance. From the above, hypotheses 2, 3, and 4 are supported.
Conclusion
In our research, we have analyzed the industry's use of strategic management tools and strategies in Singaporean organizations, examining the extent of use and the relationship between attention to tools and organizational performance. After subjectively strategic management tools and techniques (Qehaja et al. 2017) showed that the SWOT study was used most frequently in 22 studies (88%) of the 25 studies worldwide. Our research also indicated that SWOT research is viewed as a tool and strategy with a high rate of use in both the manufacturing (first) and retail (third) businesses in Singapore organizations. On the other hand, VRIO's research and strategy material had the lowest usage rate. However, it is not comprehensive as it is a moderately new, well-established tool and other research tools.
The theory suggests some approaches:
Managers in manufacturing are more likely to use strategic management tools and techniques than in retail (14 tools out of 26 tools), and normal usage is also high.
- If the number of strategic management tools and methods used by the organization is high, the organizational performance is higher.
- If the organization's managers have a solid premium in management technique, the higher the organizational performance.
- The more organizational managers become more aware of the suitability of the management strategy tools, the higher the organizational performance.
For dynamism, managers and presidents must select the appropriate approach and collect a large amount of data both inside and outside the organization. Managers and managers should be interested in, knowledgeable with, and apply a variety of strategic management tools as needed, according to the findings of this study. In order to illustrate the contrasts between the industries, it will be necessary to differentiate the disparities that appear when contrasting the assistance business and the discount company.
Furthermore, some techniques will need to be examined, such as when specific strategic management tools and processes are employed, their appropriateness, limits, and challenges.
Author: Malcolm Rozario
References
Anbumozhi, V., & Kimura, F. (2020). Regional frameworks for advancing supply chain resilience and business continuity plans. In Supply Chain Resilience (pp. 307-338). Springer, Singapore. Retrieved 7 November 2021, from https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-2870-5_12
Arbelo, A., Arbelo-Pérez, M., & Pérez-Gómez, P. (2021). Profit efficiency as a measure of performance and frontier models: a resource-based view. BRQ Business Research Quarterly, 24(2), 143-159. Retrieved 3 November 2021, from: https://doi.org/10.1177/2340944420924336
Babenko, V., Kulczyk, Z., Perevosova, I., Syniavska, O., & Davydova, O. (2019). Factors of the development of international e-commerce under the conditions of globalization. In SHS Web of Conferences (Vol. 65, p. 04016). EDP Sciences. Retrieved 3 November 2021, from: https://doi.org/10.1051/shsconf/20196504016
Berisha Qehaja, A., Kutllovci, E., & Shiroka Pula, J. (2017). Strategic management tools and techniques: A comparative analysis of empirical studies. Croatian Economic Survey, 19(1), . Retrieved 3 November 2021, from: http://dx.doi.org/10.15179/ces.19.1.3
Berisha Qehaja, A., Kutllovci, E., & Shiroka Pula, J. (2017). Strategic management tools and techniques usage: a qualitative review. Acta Universitatis Agriculturae et Silviculturae Mendelianae Brunensis, 65(2). Retrieved 7 November 2021, from https://doi.org/10.11118/actaun201765020585
Chou, S., Chen, C. W., & Kuo, Y. T. (2018). Flexibility, collaboration and relationship quality in the logistics service industry: An empirical study. Asia pacific Journal of marketing and logistics. Retrieved 7 November 2021, from https://doi.org/10.1108/APJML-08-2017-0170
Choudhary, S., Nayak, R., Dora, M., Mishra, N., & Ghadge, A. (2019). An integrated lean and green approach for improving sustainability performance: a case study of a packaging manufacturing SME in the UK. Production planning & control, 30(5-6), 353-368. Retrieved 7 November 2021, from https://doi.org/10.1080/09537287.2018.1501811
Chuang, S. H., & Lin, H. N. (2017). Performance implications of information-value offering in e-service systems: Examining the resource-based perspective and innovation strategy. The Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 26(1), 22-38. Retrieved 7 November 2021, from https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsis.2016.09.001
Demir, F. (2018). A strategic management maturity model for innovation. Technology innovation management review, 8(11). Retrieved 3 November 2021, from: http://doi.org/10.22215/timreview/1196
Gallo, P., Mihalčová, B., Gallo Jr, P., Čabinová, V., & Tomčíková, Ľ. (2019). APPLICATION OF THE BALANCED SCORECARD AS A STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT TOOL IN PRACTICE: A CASE OF SLOVAK TOURISM SECTOR. GeoJournal of Tourism and Geosites, 24 (1), 19–28. GeoJournal of Tourism and Geosites, 19.. Retrieved 3 November 2021, from: http://dx.doi.org/10.30892/gtg.24102-339
Guerola-Navarro, V., Oltra-Badenes, R., Gil-Gomez, H., & Gil-Gomez, J. A. (2021). Research model for measuring the impact of customer relationship management (CRM) on performance indicators. Economic Research-Ekonomska Istraživanja, 34(1), 2669-2691. Retrieved 3 November 2021, from: https://doi.org/10.1080/1331677X.2020.1836992
GURL, E. (2017). SWOT analysis: A theoretical review. Retrieved 3 November 2021, from: http://dx.doi.org/10.17719/jisr.2017.1832
Hassink, R., Isaksen, A., & Trippl, M. (2019). Towards a comprehensive understanding of new regional industrial path development. Regional Studies. Retrieved 7 November 2021, from https://doi.org/10.1080/00343404.2019.1566704
Hosono, A. (2020). Kaizen Toward Learning, Transformation, and High-Quality Growth: Insights from Outstanding Experiences. In Workers, Managers, Productivity (pp. 45-67). Palgrave Macmillan, Singapore. Retrieved 7 November 2021, from https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-0364-1_6
Jovanović, T., Dražić-Lutilsky, I., & Vašiček, D. (2019). Implementation of cost accounting as the economic pillar of management accounting systems in public hospitals–the case of Slovenia and Croatia. Economic research-Ekonomska istraživanja, 32(1), 3754-3772. Retrieved 7 November 2021, from https://doi.org/10.1080/1331677X.2019.1675079
Kumar, N., & Ganguly, K. K. (2020). Non-financial e-procurement performance measures: Their interdependence and impact on production cost. International Journal of Productivity and Performance Management. Retrieved 7 November 2021, from https://doi.org/10.1108/IJPPM-07-2019-0353
Madsen, D. Ø., Berg, T., Stenheim, T., Moum, J. V., Bordewich, I. O., & Storsveen, M. (2019). The long-term sustainability of lean as a management practice: Survey evidence on diffusion and use of the concept in Norway in the period 2015–2017. Sustainability, 11(11), 3120. Retrieved 7 November 2021, from https://doi.org/10.3390/su11113120
Păvălașcu, N. S., & Gabor, M. R. (2020). A Case Study on the Particularities and Sustainability of the Concepts of TQM, Quality Control, and Risk Management in the Corporate Insurance Industry: Loss and the Incidence of Catastrophic Risks. In Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute Proceedings (Vol. 63, No. 1, p. 3). Retrieved 3 November 2021, from: http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020063003
Pu, R., Teresians, D., Pieczulis, I., Kong, J., & Yue, X. G. (2021). The Interaction between Banking Sector and Financial Technology Companies: Qualitative Assessment—A Case of Lithuania. Risks 9: 21. Retrieved 7 November 2021, from https://doi.org/10.3390/risks9010021
Qehaja, A.B., Kutllovci, E., & Pula, J.S. (2017). Strategic Management Tools and Techniques Usage: a Qualitative Review, Acta Universitatis Agriculturae et Silviculturae Mendelianae Brunensis, 65(2), 585- 600.
Quah, J. S. (2018). Why Singapore works: five secrets of Singapore’s success. Public Administration and Policy. Retrieved 7 November 2021, from https://doi.org/10.1108/PAP-06-2018-002
Runge, M., Snow, R. W., Molteni, F., Thawer, S., Mohamed, A., Mandike, R., ... & Pothin, E. (2020). Simulating the council-specific impact of anti-malaria interventions: a tool to support malaria strategic planning in Tanzania. PloS one, 15(2), e0228469. Retrieved 7 November 2021, from https://doi.org/10.1371/journal. pone.0228469
Song, X., Yang, S., Huang, Z., & Huang, T. (2019, August). The Application of Artificial Intelligence in Electronic Commerce. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series (Vol. 1302, No. 3, p. 032030). IOP Publishing.. Retrieved 3 November 2021, from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1302/3/032030
Windschitl, M., Thompson, J., & Braaten, M. (2020). Ambitious science teaching. Harvard Education Press. Retrieved 7 November 2021, from https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=iDT-DwAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PT6&dq=%E2%80%9CThe+strategy+tool+is+used+to+involve+the+full+range+of+ideas&ots=ob3r8k6QPN&sig=q8gts93Q7UFjLi3mbf1bdNKb_bI